|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SENSOR INPUTS:
|
Es =
|
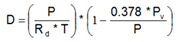
|
|
|
DEW
POINT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Temperature =
|
|
C
|
|
|
Es =
|
|
Pascals (Pa)
|
= saturation pressure of water vapor
|
td =
|
243.12*H/(17.62-H)
|
°C
|
|
|
|
|
RH % =
|
|
%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H =
|
(log10(RH)-2.0)/0.4343+(17.62*T)/(243.12+T)
|
|
|
|
|
Pressure =
|
|
Pascals (Pa)
|
if
equal to "0", altitude is used in calc
|
Tc =
|
|
temperature, deg C
|
|
td =
|
|
°C
|
= Dew Point Temperature
|
|
|
|
|
h =
|
|
meters
|
altitude above Sea Level
|
|
c0 =
|
6.1078
|
|
|
H =
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
c1 =
|
7.5
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ρ =
|
|
|
= air density
|
|
c2 =
|
237.3
|
|
|
RH % =
|
|
|
|
|
|
ρ =
|
|
|
|
kg/m3
|
Air Density
|
|
|
|
|
Temp =
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Pv =
|
Rh*Es
|
|
= actual water vapor pressure
|
m =
|
17.62
|
|
|
|
|
D =
|
density, kg/m3
|
|
|
Pv =
|
|
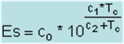
|
|
Tn =
|
243.12
|
°C
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pd =
|
pressure of dry air
(partial pressure), Pascals
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pv=
|
pressure of water vapor
(partial pressure), Pascals
|
|
|
Es =
|
|
|
|
|
P =
|
Pd +
Pv = total air pressure, Pascals ( multiply mb by 100 to get Pascals)
|
RH % =
|
|
|
|
|
Rd
=
|
287.05
|
gas constant for dry air,
J/(kg*degK) = 287.05 = R/Md
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rv
=
|
461.495
|
gas
constant for water vapor, J/(kg*degK) = 461.495 = R/Mv
|
P @ Alt & Temp =
|
|
Pascals (Pa)
|
|
|
R =
|
8314.32
|
universal
gas constant = 8314.32 (in 1976 Standard Atmosphere)
|
P =
|
|
Pascals (Pa)
|
= absolute atmospheric pressure
|
|
|
Md =
|
28.964
|
molecular weight of dry air = 28.964
gm/mol
|
|
h =
|
|
meters
|
altitude above Sea Level
|
|
|
Mv =
|
18.016
|
molecular weight of water vapor = 18.016
gm/mol
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T =
|
temperature, deg K = deg
C + 273.15
|
|
|
HUMIDITY Density Multiplier =
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Standard Atmosphere
|
|
|
p0=
|
101325
|
Pa
|
|
|
|
|
T0=
|
288.15
|
K
|
|
|
|
|
ρ0=
|
1.225
|
kg/m³
|
|
|
|
|
To calculate the density of air as a function of
altitude, one requires additional parameters. They are listed below, along
with their values according to the International
Standard Atmosphere, using the universal gas constant instead
of the specific one:
|
|
| |
|
Temperature at altitude h meters above sea level is
given by the following formula (only valid inside the troposphere):
|
|
 T
standard = T
standard =
|
|
K
|
|
|
T Non-standard =
|
|
K
|
|
|
|
|
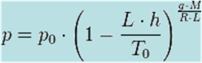
|
|
The pressure at
altitude h is given by.
|
|
|
|
|
g*M/R/L =
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
p =
|
|
Pa
|
|
|
|
|
|
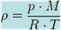
|
|
Density can then be calculated according to a molar form of the
original formula.
|
|
|
|
|
ρ =
|
|
kg/m3
|
|
|
|
|
ρ_non_std_temp
=
|
|
kg/m3
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Temp =
|
|
C
|
ambient temperature
|
|
|
|
|
h =
|
|
meters
|
Altitude above sea level
|
|
|
|
|
p0 =
|
101325
|
Pa
|
sea level standard atmospheric
pressure
|
|
|
|
T0 =
|
288.15
|
K
|
sea level standard temperature
|
|
|
|
|
g =
|
9.80665
|
m/s2
|
Earth-surface gravitational
acceleration
|
|
|
|
L =
|
0.0065
|
K/m
|
temperature lapse rate
|
|
|
|
|
R =
|
8.31447
|
J/(mol·K)
|
universal gas constant
|
|
|
|
|
M =
|
0.0289644
|
kg/mol
|
molar mass of dry
air
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
